The rapid evolution of modern electronics has necessitated innovative design solutions that marry functionality with compactness. One of the key advancements in this arena is the adoption of flexible PCB (printed circuit boards), which have gained significant traction due to their inherent advantages over traditional rigid counterparts. According to a report by the market research firm, ResearchAndMarkets, the global flexible PCB market is projected to reach $29.4 billion by 2025, highlighting the increasing reliance on these adaptable circuits in various applications, from consumer electronics to medical devices.
Flexible PCBs enable designers to create slimmer, lighter products while maintaining optimal performance. Their unique properties allow them to be integrated into complex geometries and confined spaces, making them ideal for high-density electronic designs. Furthermore, a study published in the Journal of Electronic Materials indicates that flexible PCBs can enhance the reliability and longevity of devices, as they are less susceptible to mechanical stress and environmental factors. This combination of flexibility, durability, and performance positions flexible PCBs as a cornerstone of modern electronics, paving the way for innovative developments across multiple sectors.

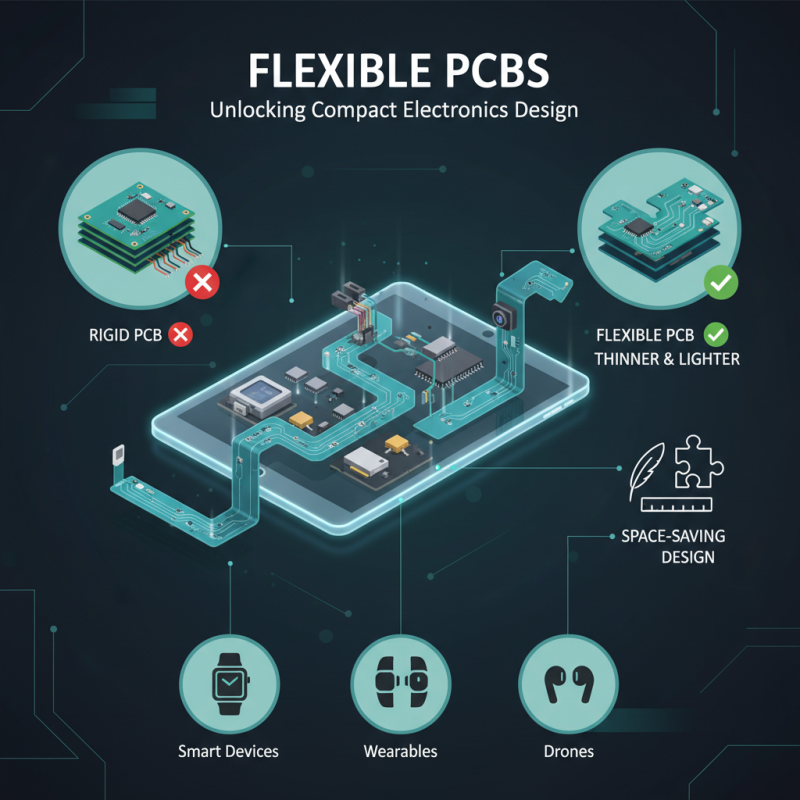
Flexible PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) have become a game-changer in the realm of electronics design, particularly for applications requiring space-saving solutions. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs can be bent and shaped to fit complex contours, making them ideal for compact devices. This flexibility allows designers to optimize the use of available space, enabling the creation of thinner, lighter products without sacrificing performance or functionality. As a result, the versatility of flexible PCBs supports innovative design approaches that are particularly beneficial in modern consumer electronics, where the demand for miniaturization is continuous.
Moreover, the incorporation of flexible PCBs can significantly enhance the density of electronic components in a design. By allowing multiple layers to be stacked or arranged in unique geometries, these PCBs enable a higher concentration of circuits in a reduced area. This arrangement not only saves precious space but also improves signal quality by minimizing the length of connections, thereby reducing potential interference. The ability to integrate multiple functionalities onto a single, flexible substrate furthers the evolution of devices such as wearables, smartphones, and medical gadgets, emphasizing their crucial role in the future of compact electronic solutions.
Flexible PCBs are becoming increasingly integral in modern electronics design, especially due to their enhanced durability and reliability in harsh environments. These unique circuit boards are made from flexible substrates, allowing them to withstand extreme temperatures, vibrations, and mechanical stresses that traditional rigid PCBs cannot endure. This adaptability makes flexible PCBs ideal for applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices, where reliability is paramount. Their ability to bend and conform to various shapes without compromising functionality ensures that they can perform well even in the most demanding conditions.
In addition to their physical resilience, flexible PCBs also exhibit superior electrical performance. The reduced weight and space-saving design contribute to a more efficient layout, which enhances signal integrity and minimizes electromagnetic interference. This is particularly beneficial in high-frequency applications, where even the slightest degradation in performance can lead to significant operational issues. As a result, flexible PCBs not only support advanced electronic functionalities but also remain reliable over extended operational periods, making them a critical component in the evolution of electronics in challenging environments.
The manufacturing process for flexible printed circuits (PCBs) has evolved significantly, making it a cost-effective solution for modern electronics design. Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs can be produced using a variety of techniques that optimize material usage and reduce waste. The ability to utilize thin, lightweight materials not only cuts down on production costs but also makes shipping and handling more economical. As the demand for compact and lightweight electronic devices increases, manufacturers are finding it advantageous to adopt flexible PCB technologies to meet these contemporary needs.
Moreover, the streamlined production processes associated with flexible PCBs can significantly shorten lead times. Techniques such as roll-to-roll processing enable high-volume production with fewer interruptions, allowing companies to respond quickly to market demands. This efficiency in manufacturing not only lowers costs but also enhances design flexibility, enabling engineers to innovate without being hindered by production constraints. By focusing on these cost-effective manufacturing processes, businesses can develop more competitive products that enhance functionality while optimizing their budget.
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Design |
|---|---|---|
| Space Saving | Flexible PCBs can conform to different shapes, allowing for more compact designs. | Enables miniaturization of devices, critical in portable electronics. |
| Weight Reduction | Lighter materials lead to overall reduced product weight. | Enhances mobility and reduces shipping costs. |
| Improved Reliability | Less stress on components due to flexibility, reducing the risk of failure. | Higher durability and longer lifespan of electronic devices. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower manufacturing costs due to simplified assembly processes. | Reduced overall production costs for manufacturers. |
| Design Flexibility | Support for complex and multi-layered circuit designs. | Encourages innovative product designs. |
| Lower Assembly Costs | Reduced labor costs due to easier assembly processes. | More cost-effective production line operations. |
| Enhanced Performance | Better electrical performance due to shorter connection paths. | Improves overall device functionality. |
| Thermal Management | Flexible circuits dissipate heat more efficiently. | Prevents overheating in compact designs. |
| Future-Proofing | Flexible PCBs can easily adapt to new technologies and designs. | Sustains relevance in rapidly evolving markets. |
Flexible printed circuit boards (PCBs) have revolutionized modern electronics design, particularly in terms of their enhanced thermal management capabilities. Unlike traditional rigid boards, flexible PCBs can be designed to cover complex shapes and conform around heat-intensive components. This flexibility allows for better heat dissipation, preventing localized overheating which can lead to premature component failure. The material composition and layout of flexible PCBs can be engineered to promote efficient thermal pathways, effectively transferring heat away from sensitive areas and distributing it across a larger surface area.
Moreover, the lightweight nature of flexible PCBs contributes to their thermal efficiency. With minimal thermal mass, they respond quickly to changes in temperature, allowing for real-time thermal management. This is especially beneficial in high-power applications such as consumer electronics and automotive systems, where overheating can drastically affect performance and safety. By integrating advanced thermal management designs into flexible PCBs, engineers can create more reliable, longer-lasting devices, enhancing overall functionality and performance in a wide range of applications.
This bar chart illustrates the top 10 benefits of using Flexible PCBs in modern electronics design. Each benefit is rated on a scale from 1 to 10 based on its significance in enhancing electronic device performance and design efficiency.

Flexible PCBs offer unparalleled design versatility, enabling infinite configurations that cater to a wide range of modern electronics applications. According to a report from the IPC, the global flexible printed circuit board market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.6% from 2021 to 2026, highlighting growing demand in sectors like consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices. This adaptability allows engineers to develop intricate designs that fit into unconventional spaces, creating opportunities for more compact and lightweight devices without compromising functionality.
Designers can create layouts that would be impossible with traditional rigid circuit boards, utilizing the flexibility to navigate complex geometries and tight spaces. This capability is particularly beneficial in the development of portable electronics and wearables, where space is at a premium. The use of flexible PCBs also facilitates the integration of multiple components into a single unit, reducing assembly time and improving overall device reliability.
Tip: When designing with flexible PCBs, consider the use of virtual prototyping software to visualize configurations and minimize errors early in the design process.
Furthermore, flexible PCBs can withstand bending and twisting, making them ideal for applications that require continuous motion, such as in robotics or foldable devices. By incorporating flexible designs, companies can enhance product durability while also delivering innovative features that meet the evolving demands of consumers.
Tip: Always assess the environmental conditions your flexible PCB will face, such as temperature and humidity, to select appropriate materials that ensure longevity and performance.



| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |