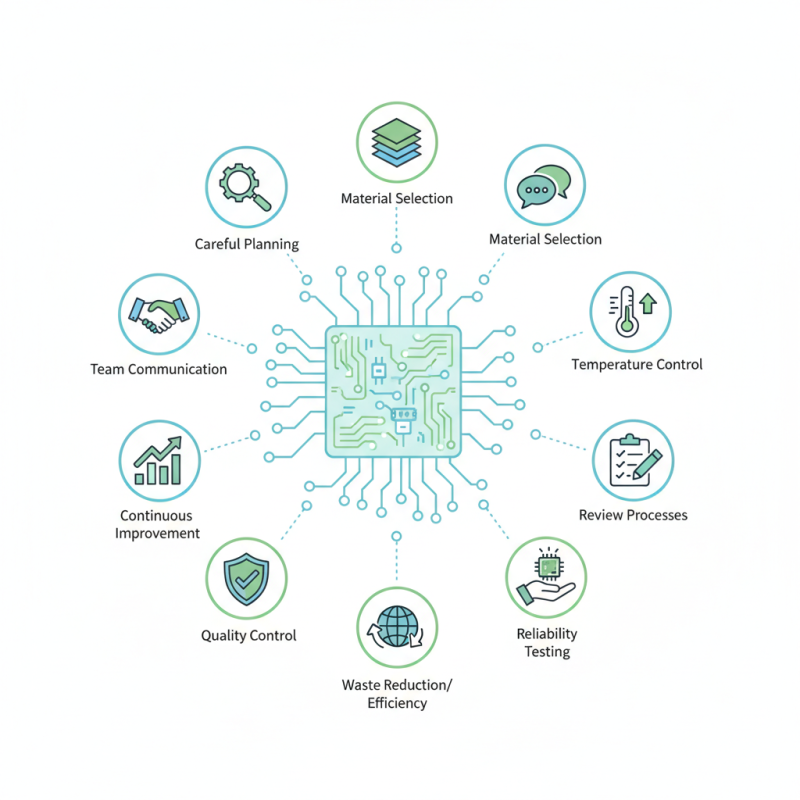
In the fast-paced world of electronics, effective pcb manufacturing and assembly techniques are vital. These processes determine the performance and reliability of electronic devices. Companies aim for high quality and low costs, yet mistakes can happen. Careful planning and execution are necessary to achieve this delicate balance.
Whether you are a novice or an experienced engineer, understanding essential tips can lead to significant improvements. Many overlook details like material selection and temperature control. These elements play a key role in ensuring durability and efficiency. Inadequate attention can result in costly errors.
Moreover, communication within teams is crucial. Misunderstandings can lead to faulty designs or delays. Review processes are often neglected, but they are essential to refining results. By adopting a mindset of continuous improvement, organizations can elevate their pcb manufacturing and assembly practices. This journey involves learning from past mistakes and seeking innovative solutions.
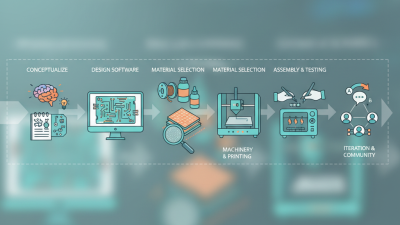
Understanding PCB design fundamentals is crucial for successful manufacturing. Designers must grasp the importance of layout efficiency. Every trace counts. They need to be mindful of the spacing between components. Too close can cause interference. Too far may create signal integrity issues.
Another key aspect is the selection of appropriate materials. Materials can greatly impact the performance and reliability of the PCB. Designers often overlook thermal management. Heat dissipation must be considered early in the design stage. Flaws in this area can lead to catastrophic failures. Adjustments might be necessary after initial prototypes are tested.
Communication between teams is often inadequate. This can result in misunderstandings regarding design intent and manufacturing capabilities. A collaborative approach can bridge these gaps. Regular reviews and feedback loops are valuable. They ensure that designs are not only functional but also manufacturable. Emphasizing these principles can significantly improve manufacturing outcomes.
| Tip | Description | Importance | Best Practices |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Design for Manufacturability (DFM) | Ensure your PCB layout is optimal for manufacturing processes. | High | Use standard components and minimize intricate designs. |
| 2. Select the Right Materials | Choose appropriate substrates and finishes to meet performance needs. | Medium | Consult with suppliers for best material options. |
| 3. Utilize Simulation Tools | Simulate designs to detect potential issues before production. | High | Invest in robust PCB simulation software. |
| 4. Optimize PCB Layout | Arrange components logically to minimize signal interference. | High | Follow best practices for trace routing and component placement. |
| 5. Ensure Proper Solder Mask Application | Use the right solder mask to protect against short circuits. | Medium | Choose high-quality materials for solder mask. |
| 6. Conduct thorough testing | Test PCBs for reliability under different conditions. | High | Implement both functional and environmental testing. |
| 7. Focus on Documentation | Maintain comprehensive documentation for manufacturing processes. | Medium | Create detailed design files and assembly instructions. |
| 8. Choose Experienced Assembly Partners | Partner with reputable assembly services for quality results. | High | Research and vet assembly partners thoroughly. |
| 9. Implement Quality Control Measures | Establish quality benchmarks and monitor throughout the process. | High | Use statistical process control (SPC) techniques. |
| 10. Stay Updated with Industry Trends | Keep abreast of the latest technologies and methods in PCB manufacturing. | Medium | Attend industry seminars and workshops regularly. |
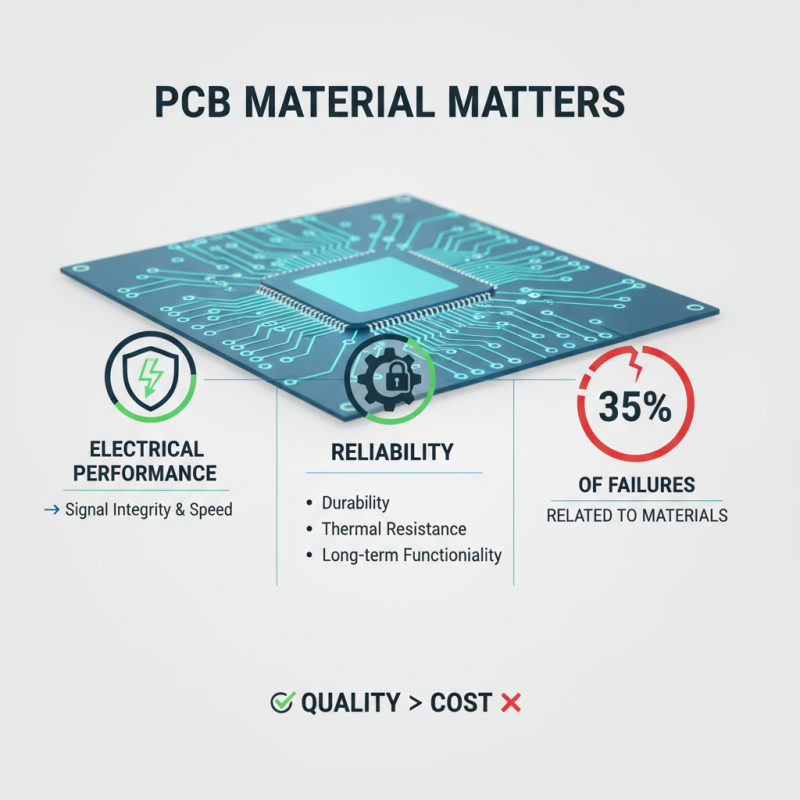
Choosing the right materials is crucial in PCB production. The material affects electrical performance and reliability. A recent report stated that 35% of PCB failures relate to material issues. Quality matters more than ever.
FR-4 is the most common material, but alternatives exist. Polyimide or Rogers can offer higher performance in demanding environments. Each material has unique thermal and electrical properties. The wrong choice can lead to inefficiencies, increased costs, and failure rates.
Furthermore, consider surface finishes carefully. OSP, ENIG, or HASL can influence solderability and longevity. The market trends show a rising demand for lead-free options. Yet, not all methods perform identically under stress. It’s vital to test materials before full-scale production. Balancing cost with performance can be challenging, but it is necessary. Rushed decisions can lead to subpar outcomes.
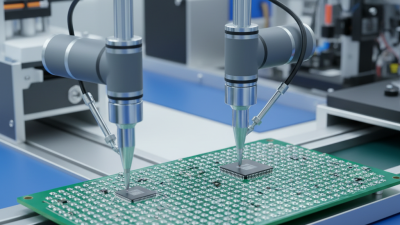
Soldering and component placement are critical in PCB manufacturing. Precision in these areas directly impacts the functionality and reliability of electronic devices. According to a report by IPC, nearly 60% of PCB failures arise from poor soldering practices. This statistic highlights the need for meticulous attention during assembly.
Improper soldering techniques can lead to cold joints or bridging. These defects often result in circuit failures. A study indicated that optimizing solder temperature and time can decrease defects by up to 40%. Maintaining an environment with controlled humidity can also enhance solder quality. Small changes can yield significant improvements in overall product reliability.
Component placement demands accuracy and speed. Automated placement machines are essential, yet they are not infallible. Mistakes can occur, particularly with small or multiple-layer boards. Research suggests that even a 1% deviation in component placement can lead to performance issues. Continual training for operators on best practices is vital. Regular assessments of equipment performance are also necessary. Balancing speed and precision often involves trade-offs, necessitating constant improvement in processes.

Quality control is vital in PCB manufacturing and assembly. It ensures the product meets industry standards. Inspecting raw materials is the first step. Every batch should be checked for defects. A small flaw can lead to significant issues. This review is crucial to prevent problems later on.
During assembly, strict guidelines must be followed. Automated optical inspection (AOI) can help detect errors. It scans completed boards for misplaced components. However, visual inspections also play a role. Human eyes can catch mistakes machines may miss. Regular training for staff ensures everyone is vigilant.
Documentation is another key area for quality control. Proper records of each manufacturing step should be kept. This creates a traceable path for any issues that arise. Mistakes in documentation can cause delays. Reflecting on these issues can lead to growth and improvement. Quality control is not just a checklist; it’s an ongoing process that requires constant attention.
Testing and inspecting finished PCBs is crucial for ensuring their reliability and performance. Visual inspection should be the first step. This helps identify any visible defects. Inspectors need to check for solder joints, component placements, and traces. Using magnification tools can greatly enhance this process. Sometimes, flaws are not easy to spot. A careful examination ensures a higher standard of quality.
Next, functional testing becomes vital. This involves powering up the PCB and verifying its operation against specifications. However, not all issues manifest immediately. Some defects may only emerge under certain conditions. It’s essential to simulate the operating environment. Environmental testing can also uncover hidden weaknesses. Humidity and temperature changes can affect performance.
Automated testing methods can aid in efficiency. These techniques help identify faults quickly. However, reliance on automation alone can be risky. Skilled technicians bring a critical perspective that machines cannot replicate. Experienced individuals can spot anomalies that technology might miss. Relying solely on machines could lead to oversight. Balancing technology with human expertise is key to effective PCB manufacturing.

| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |