In the realm of electronics manufacturing, pcb assembly plays a vital role. It involves the process of placing electronic components onto a printed circuit board. This process is crucial for ensuring functionality and reliability. Without proper pcb assembly, devices may fail to operate as intended.
The precision in pcb assembly affects the overall quality of electronic products. Each component must be accurately placed and soldered. This requires careful attention to detail, as small errors can lead to significant problems. For instance, improper solder joints can cause short circuits or device malfunctions.
Moreover, the growing complexity of electronic devices challenges manufacturers. They must adapt to innovative designs and technologies. Keeping pace with these changes is essential. Even minor miscalculations in the pcb assembly process can result in costly delays and recalls. Reflecting on these challenges can help manufacturers improve their practices. It’s an ongoing journey of refinement and adaptation in the pursuit of excellence.
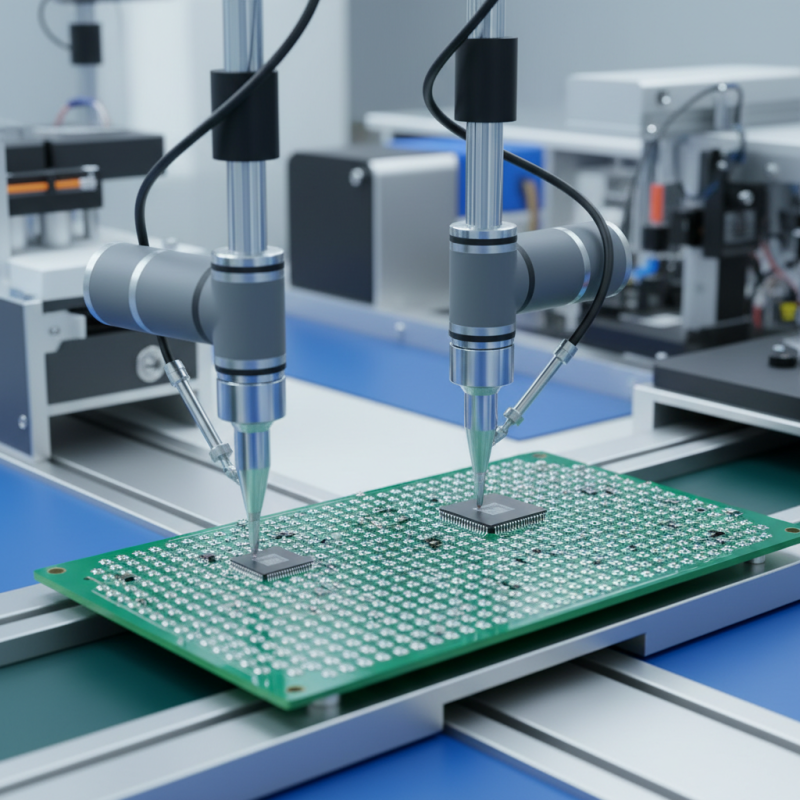
PCB assembly is a crucial step in electronics manufacturing. It transforms a bare circuit board into a functional device. This process integrates various components like capacitors, resistors, and integrated circuits. According to market research, the global PCB market is expected to reach $75 billion by 2025. This growth highlights how essential PCB assembly is in driving innovation across industries.
One significant factor is efficiency. A well-executed PCB assembly can help reduce overall production costs. A report from IPC indicates that well-optimized processes can shrink assembly time by up to 30%. However, quality issues can arise if proper standards are not maintained. Misalignments and poor soldering can lead to device failures. Such mistakes often increase rework rates, which can negate any cost savings.
Moreover, complexity increases with miniaturization. As devices become smaller, PCB designs grow more intricate. This trend demands advanced assembly techniques. Failure to adopt these can hinder product performance. A staggering 50% of manufacturers report difficulties in handling miniaturized assemblies. Addressing these challenges is vital for sustaining competitive advantage in a fast-evolving market. Therefore, prioritizing quality in PCB assembly is more than just a checklist item; it's a necessity.
The PCB assembly process is crucial in electronics manufacturing. It involves several components that work together to create functional electronic devices. Key components include printed circuit boards (PCBs), integrated circuits (ICs), resistors, capacitors, and connectors. Each element must be precise in placement and soldering. A minor error can lead to significant failures in the final product.
Industry studies show that approximately 70% of electronic failures stem from poor PCB assembly quality. The need for careful inspection and testing is vital. Advanced computer systems and solder technologies have improved assembly accuracy. However, human error still occurs, often due to rushed production schedules or miscommunication. Inspectors must rigorously analyze each board.
**Tip:** Always verify the specifications of components before assembly. This step saves time and reduces errors later on.
In the assembly line, automation plays a critical role. Automated machines ensure high precision, yet they cannot catch every error. Human oversight remains essential. Regular training for assembly staff is necessary to maintain high standards.
**Tip:** Keep a checklist for common assembly pitfalls. This can help mitigate mistakes.
Overall, integrating technology in PCB assembly can enhance the production process. Yet, human factors cannot be overlooked. Balancing both aspects is the key to successful electronics manufacturing.
In PCB assembly, quality control is crucial. Ensuring the reliability of electronic devices starts at this stage. A 2021 report highlights that about 30% of electronic failures come from poor PCB assembly. This statistic underscores the importance of rigorous quality checks throughout the process.
Implementing various quality control measures can reduce errors significantly. Automated optical inspection (AOI) is one method commonly used. It detects issues like solder joint defects. A study indicates that AOI can enhance defect detection rates by up to 50%. This is vital, especially where high-density interconnections are present.
Furthermore, manual inspections still play an essential role. While they are less accurate than AOI, human oversight can catch faults that machines might miss. However, quality control isn't foolproof. Some defects can elude both AOI and human inspectors. It's a reminder that continuous improvement is necessary. Regular training for assembly workers can also enhance outcomes. A skilled workforce can adapt to new technologies and changing designs.
Therefore, ongoing education becomes a crucial element in maintaining high-quality PCB assemblies. Balancing automation with skilled labor fosters a more reliable manufacturing process.

Technological advancements have transformed PCB assembly in recent years. Automation and robotics play a crucial role in enhancing efficiency. Machines are faster and more accurate. They can place components with precision. However, reliance on machines may overlook human intuition, which sometimes detects subtle issues.
Moreover, computer software has improved design capabilities. Engineers can simulate and test designs before actual production. This reduces errors and rework. Yet, the complexity of software can lead to miscommunication among teams. Sometimes, a simple oversight can cause delays.
Another fascinating aspect is miniaturization. Components are becoming smaller and more intricate. This trend allows for more compact designs. However, it poses challenges in assembly processes. Smaller components require stricter handling protocols. It’s easy to overlook specifications. Mistakes can result in significant setbacks in production.
The electronics industry is rapidly evolving. PCB assembly plays a critical role in this transformation. As devices become more compact, the demand for precision in PCB design grows. This trend raises questions about efficiency and reliability. Can manufacturers keep pace with such rapid changes?
Automation is becoming a standard in PCB assembly. Machines now handle placements quicker than humans. However, this shift brings challenges. Errors can occur during the programming of these machines. A small miscalculation leads to significant issues. Quality control remains essential to ensure accuracy. The industry must prioritize training for operators to manage these technologies effectively.
Additionally, sustainability is a rising concern in electronics manufacturing. Companies need to focus on eco-friendly materials and processes. This commitment can reduce waste and enhance public perception. Yet, the transition can be costly for many firms. Balancing cost and sustainability is a complex challenge. The future of PCB assembly is promising but requires reflection on these evolving demands.
| Aspect | Description | Future Trends | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Quality Control | Ensures high reliability and performance of circuits. | Increased use of automated inspection technologies. | Critical for reducing failures in electronic devices. |
| Component Integration | Combines multiple components into a single PCB. | Adoption of miniaturization techniques. | Enhances product functionality and reduces costs. |
| Supply Chain Efficiency | Streamlines manufacturing processes. | Utilization of smart logistics and IoT. | Essential for timely market delivery. |
| Cost Management | Helps in controlling production costs. | Emerging techniques to reduce waste. | Important for maintaining competitiveness. |
| Customization | Allows tailored solutions for specific applications. | Expansion of flexible PCB technologies. | Critical for meeting diverse customer needs. |


| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |