The PCB printing industry is evolving rapidly. Innovations are crucial for meeting the increasing demand for high-performance electronics. According to a recent report by IPC, the global printed circuit board market is expected to reach $90 billion by 2026. This growth emphasizes the need for advanced PCB printing techniques.
Emerging technologies like 3D printing and flexible PCBs are reshaping the landscape. These methods enable manufacturers to create intricate designs with enhanced efficiency. However, adapting to new techniques presents challenges. Some companies struggle with quality control during the transition.
Understanding the latest trends in PCB printing is vital. The shift towards miniaturization requires precise methods and innovative materials. Companies must remain agile and responsive to maintain a competitive edge. Balancing innovation and practicality will determine success in the evolving market.

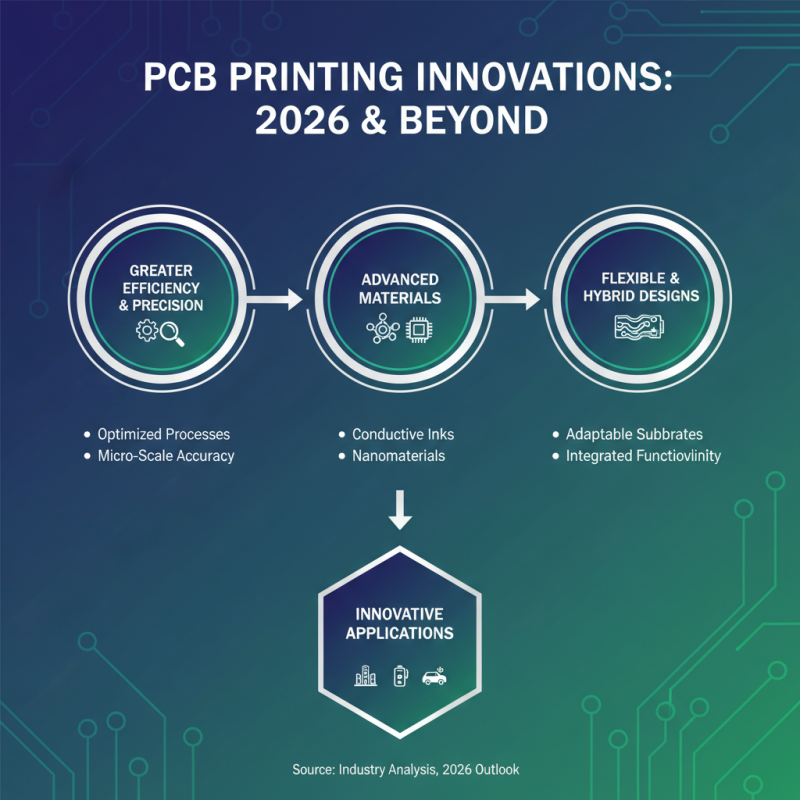
As we look ahead to 2026, the landscape of PCB printing techniques is evolving rapidly. Emerging trends emphasize greater efficiency and precision. Advanced materials are now making a significant impact. Flexible and hybrid PCBs are gaining traction, allowing for innovative designs. These materials can adapt to various applications and environments.
New printing technologies, like inkjet and laser techniques, are pushing boundaries. These methods offer fine resolution and speed. However, the learning curve remains steep. Not all manufacturers are ready to adopt these advanced techniques. The shift requires updates in tooling and training. It’s a challenge many face today.
Sustainability is another focal point. Eco-friendly inks and materials are now a priority. The industry seeks to minimize waste and reduce environmental impact. Yet, these materials can sometimes compromise performance. Finding the right balance between sustainability and efficiency is crucial. It’s clear that while the future is promising, there are hurdles that require thoughtful reflection and adaptation.
The landscape of PCB manufacturing is evolving rapidly. Innovative technologies play a crucial role in this transformation. Advanced printing techniques, such as additive manufacturing, are changing how circuits are created. These methods allow for greater precision and customization. They can reduce waste and improve efficiency. However, challenges remain in achieving consistent quality.
Moreover, techniques like inkjet and screen printing are gaining traction. These methods enable quick prototyping and production. They can adapt to different materials and designs. Yet, securing proper adhesion and reliability during assembly is an ongoing issue. Manufacturers must constantly refine these processes. Flexibility is key, but it requires investments in training and technology.
Emerging technologies, such as AI and IoT, offer new possibilities. They promise improved monitoring and data analysis in PCB production. However, the integration of such technologies is not without hurdles. Companies must navigate compatibility and workforce readiness. Balancing innovation with practical implementation is essential. The future of PCB manufacturing depends on overcoming these challenges.
In the world of printed circuit boards (PCBs), traditional methods like screen printing and etching have served well for decades. These methods often require extensive manual labor and precise skills. The printers used can be slow, and mistakes often lead to waste and rewiring. Additionally, scaling production can be challenging, as each design iteration may need a complete setup from scratch.
Modern techniques, such as direct inkjet printing and laser etching, are changing the landscape. These methods allow for rapid prototyping and flexibility. For instance, digital printing can create complex designs quickly without significant setup time. Still, many manufacturers face hurdles with quality control. Often, ink adhesion becomes an issue, leading to potential failures in circuit performance.
While these innovations show promise, they are not without flaws. Transitioning to digital methods can strain existing workflows. Training staff on new equipment brings obstacles that some companies may not be ready to tackle. Balancing cost with innovation remains crucial. Such comparisons highlight how the industry is evolving while still grappling with the challenges of adopting new technologies.
The world of PCB printing is rapidly evolving. Emerging technologies are changing traditional practices. These innovations bring both significant advantages and challenges. Enhanced precision, improved material efficiency, and faster production cycles are key benefits. Such advancements provide companies with a competitive edge in a fast-paced market. However, adapting to these new techniques requires careful consideration.
Interestingly, not all innovations are universally beneficial. For instance, some advanced printing methods may involve higher initial costs. Additionally, training staff to operate new systems effectively can be daunting. Companies must weigh the benefits against these challenges. There are also concerns regarding material compatibility and long-term reliability. It is crucial to closely monitor the performance of newly adopted practices.
Moreover, as the field grows, the learning curve can be steep. Failure to adapt can hinder progress. Some companies may overlook the importance of research and development. This could lead them to miss out on valuable opportunities. As innovations continue to unfold, ongoing evaluation will be vital. Embracing change is essential, but caution is equally important.
The future of PCB printing is evolving rapidly. Innovations are emerging that promise to reshape electronic manufacturing. Techniques like additive printing are gaining traction, allowing for more complex designs. This method reduces waste and increases customization, making it an attractive option for many. However, it is not without challenges. Reliability in high-speed applications remains a concern that needs addressing.
Moreover, the integration of AI in PCB printing is an exciting direction. AI can optimize designs and streamline production processes. It can help predict potential failures, which reduces downtime. Yet, the reliance on technology raises questions. Is the industry becoming too dependent on automation? While enhancements in efficiency are valuable, the balance between human oversight and machines must be carefully considered.
Sustainability is another critical area to reflect on. As the industry moves forward, eco-friendly materials and processes must be prioritized. The current recycling methods for PCBs are not efficient enough. Companies should invest in research to create better solutions. The future requires not just innovation but also responsible practices for a more sustainable electronic landscape.
This bar chart displays the adoption rates of various PCB printing techniques predicted for 2026. The techniques include Advanced Inkjet, Direct Imaging, and others, showing the industry's focus on innovative printing solutions.



| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |